Learn how to create RESTful Web Services with Spring Boot using this beginner-friendly guide. Includes step-by-step examples, best practices, and top interview questions for your preparation.
Imagine you and your friends are playing a game where everyone can request a candy from you. You’re in charge of handing out candies. Here’s how it works:
- A friend asks, “Can I have one candy?”
- You give them a candy if you have one, or you say, “Sorry, no candy left.”
In this example:
- You are the server (like a Spring Boot application).
- Your friends are the clients (like a browser or app).
- The candy requests are like HTTP requests.
- The candy is the data being shared.
RESTful Web Services work the same way—they enable servers (like your Spring Boot app) to share “candies” (data) with clients via HTTP.
Table of Contents
Step-by-Step Guide to Building RESTful Web Services in Spring Boot
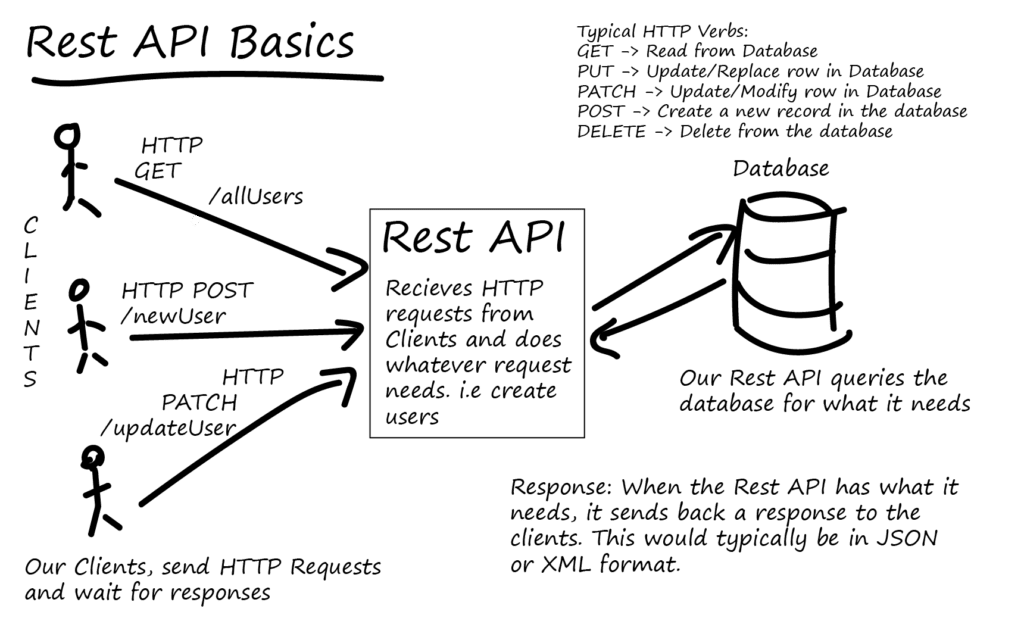
1. What is REST?
REST (Representational State Transfer) is a set of principles for designing web services.
Key principles include:
- Statelessness: Each request from a client contains all the information needed to process it.
- Resources: Data is represented as resources identified by URIs (e.g.,
/api/users). - HTTP Methods: Use HTTP verbs (GET, POST, PUT, DELETE) to interact with resources.
2. Setting Up Spring Boot Project
Go to Spring Initializr and generate a project with the following dependencies:
- Spring Web
- Spring Boot DevTools
- Lombok
Unzip and import the project into your favorite IDE.
3. Creating Your First RESTful Web Service
File: UserController.java
javaCopy codepackage com.example.demo.controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api/users")
public class UserController {
@GetMapping
public List<String> getUsers() {
return Arrays.asList("Alice", "Bob", "Charlie");
}
@PostMapping
public String addUser(@RequestBody String name) {
return "User " + name + " added successfully!";
}
@DeleteMapping("/{name}")
public String deleteUser(@PathVariable String name) {
return "User " + name + " deleted successfully!";
}
}
4. Understanding the Code
@RestController: Marks this class as a REST API controller.@RequestMapping("/api/users"): All endpoints in this controller will start with/api/users.@GetMapping: Handles HTTP GET requests to fetch user data.@PostMapping: Handles HTTP POST requests to add a new user.@DeleteMapping("/{name}"): Handles HTTP DELETE requests to remove a user by their name.
5. Testing the Endpoints
Use tools like Postman or cURL to test your RESTful API:
- GET
/api/users:
Returns a list of users:["Alice", "Bob", "Charlie"]. - POST
/api/users(Body:"David"):
Response:"User David added successfully!". - DELETE
/api/users/David:
Response:"User David deleted successfully!".
6. Best Practices for RESTful Web Services
- Use Proper HTTP Status Codes: Return appropriate status codes like
200 OK,201 Created,400 Bad Request,404 Not Found, etc. - Validate Input Data: Ensure the data received in requests is valid.
- Handle Exceptions Gracefully: Use
@ControllerAdviceto handle exceptions globally. - Enable CORS: To allow requests from different domains, configure CORS policies.
7. Common Spring Boot RESTful Web Service Interview Questions
- What is a RESTful Web Service?
A RESTful Web Service is a service that adheres to REST principles and uses HTTP methods to expose data as resources. - What is the difference between
@Controllerand@RestController?@Controlleris used for MVC-based web applications and returns views.@RestControlleris used for RESTful APIs and returns data directly as JSON or XML.
- How do you handle exceptions in Spring Boot REST APIs?
Use@ControllerAdvicealong with custom exception handler methods annotated with@ExceptionHandler. - What are the HTTP methods supported in REST?
- GET: Retrieve data.
- POST: Create data.
- PUT: Update data.
- DELETE: Remove data.
- How can you secure REST APIs in Spring Boot?
- Use Spring Security for authentication and authorization.
- Implement OAuth2 or JWT for token-based security.
- What is the purpose of
@RequestBodyand@PathVariable?@RequestBody: Maps the request payload to a method parameter.@PathVariable: Extracts values from the URI path.